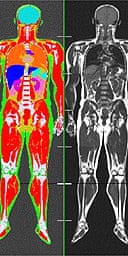
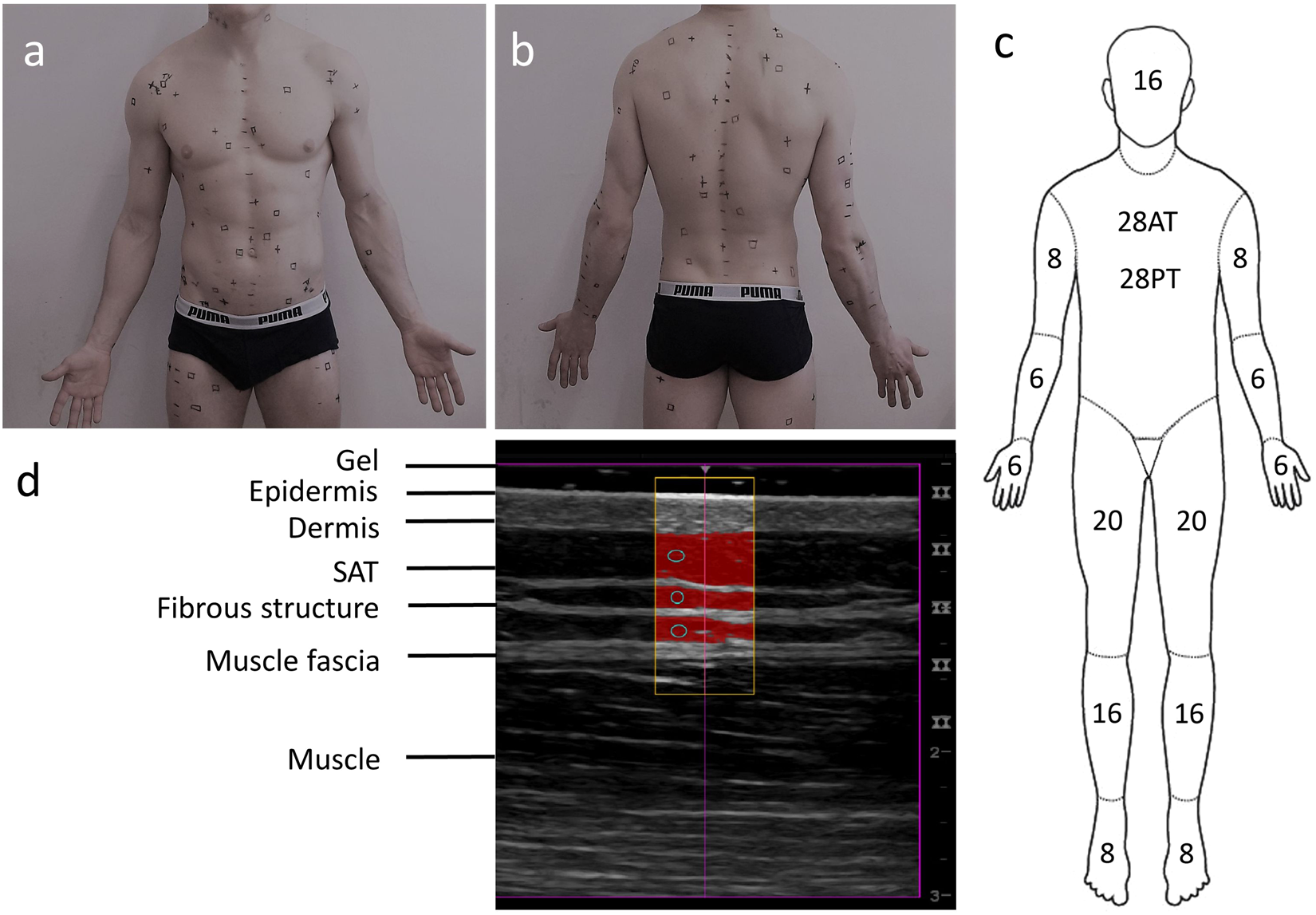
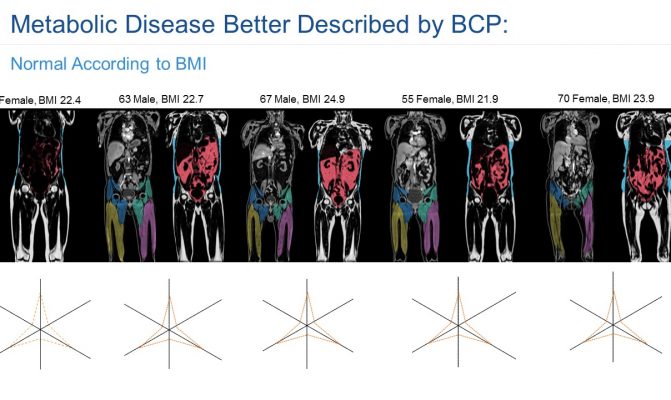
In this study we assessed different magnetic resonance imaging mri scanning regimes and examined some of the assumptions commonly made for measuring body fat content by mri. Whole body mri was used to quantify and study different body fat depots in 67 women.

Fig 10 Molecular And Cellular Biology
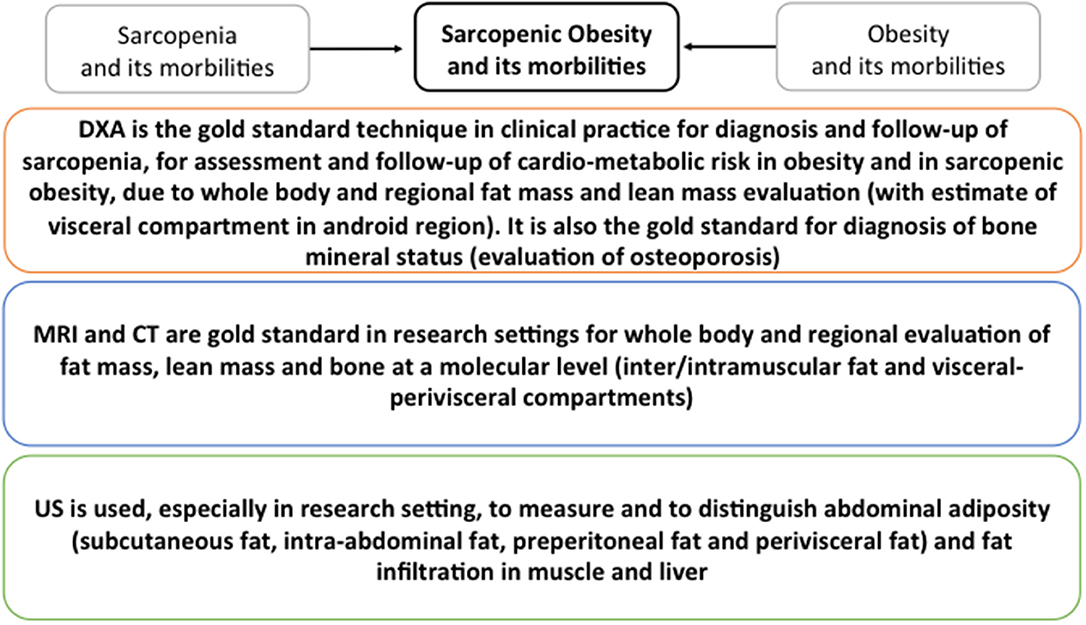
Mri body fat measurement. Compared with mri the bia underestimated the total fat with approximately 5 kg 7 kg loa on average this despite the fact that the mri based measurements of total body fat excluded the arms and lower legs. These machines take cross sectional images of. Whole body mri in conjunction with cad allows a fast automatic and accurate approach to body fat measurement and localization and can be a useful alternative to body mass index. Mri can decompose the liver signal into fat and water components and measure liver fat more directly than ultrasound or ct. Perhaps the most accurate method for determining body fat percentage is with magnetic resonance imaging mri or computerized tomography ct scans. The highest linear correlation found between bia and mri derived measures was 075 and 081 for females and males respectively.
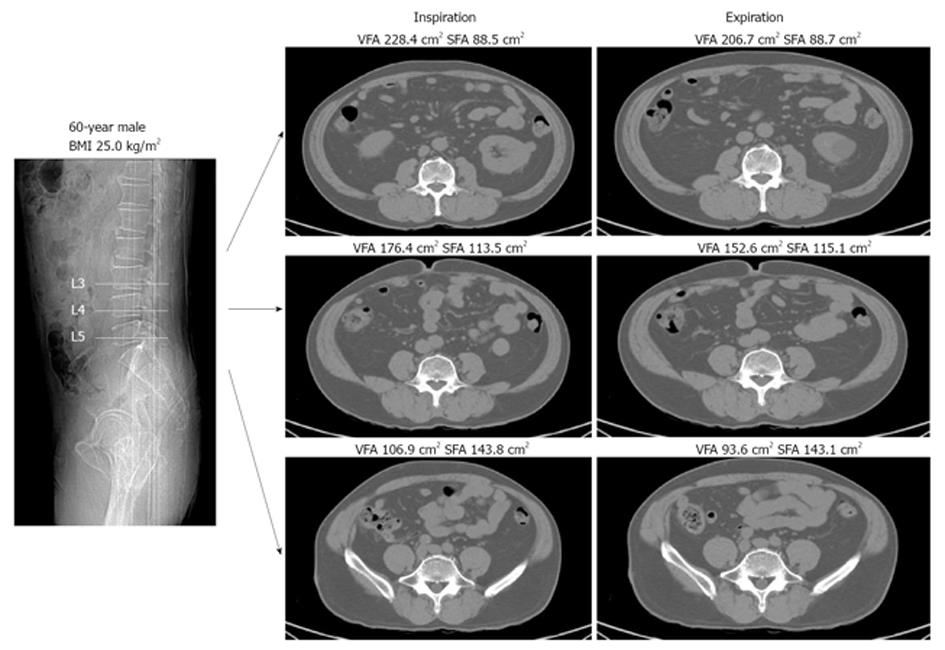
The whole body mri results showed that there was a significant variation in the percentage of total internal as well as visceral adipose tissue across a range of adiposity which could not be predicted from total body fat andor. Whole body fat analysis can be achieved in less than 5 min. Body fat can also be estimated using cross sectional imaging methods such as magnetic resonance imaging mri nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and computerized tomography ct. 29 figure 5 shows an example of hepatic imaging in a subject with hepatic steatosis and severe dyslipidemia before and after treatment of the dyslipidemia with plasmapheresis and multidrug therapy. These scans can provide the most precise body composition measurements especially for intra abdominal fat measurement.